What is a Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM)?
A CGM measures glucose levels every 5 minutes and gives information on glucose trends in the form of arrows. This information gives more insight into where the blood sugar is going and helps people make better diabetes decisions. Access to the abundance of data that CGM's provide allows for better health outcomes and has led to the change in goals for people with diabetes to be time in range versus HbA1c.
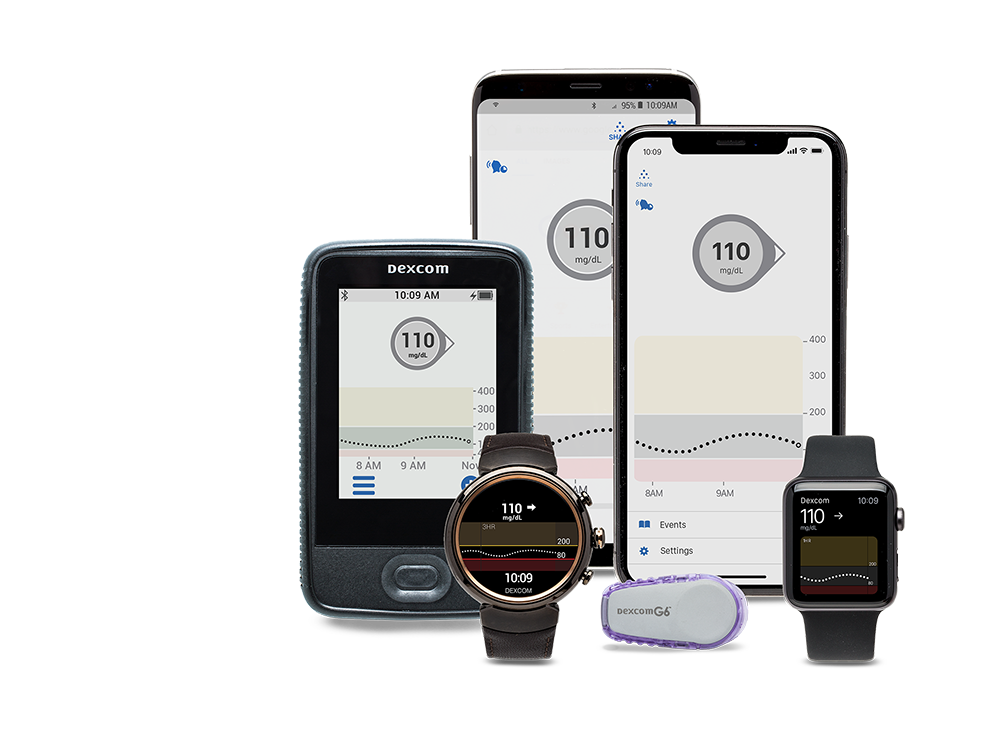
A CGM System consists of three basic parts:
- Sensor – A small sensor is inserted just beneath the skin and measures your interstitial fluid for glucose values. Insertion is similar to infusion sets for insulin pumps. Typically, a sensor is approved to wear for up to 7-14 days.
- Transmitter – A small wearable that is attached to the top of the sensor and sends glucose data wirelessly to your compatible smart device or receiver. Some are disposable, where others are reusable and need to be removed after use and replaced into the next sensor.
- Display device - A compatible smart device, insulin pump or receiver will have a display screen where you receive your current glucose number and the ability to review past and present glucose trends with your physician for better diabetes management.
Benefits of a CGM
- HbA1c Reduction: CGM has proven to be the best outpatient glycemic management system for reducing HbA1C. People with type 1 diabetes have experienced an average HbA1C reduction of 1.3%*1.
- Reduced Hypoglycemia: Not only can CGM reduce A1C, numerous studies have shown it can also decrease time spent in hypoglycemia1-3
- Alerts and Alarms: CGM Systems are equipped with alerts and alarms that notify you of approaching highs and lows
- Real-time glucose information: CGM provides real-time information about your glucose level speed and direction (high or low), so you have more insight for proactively managing your diabetes.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Products
- The Dexcom G6 CGM System can now be used in place of fingerstick testing for treatment decisions*.
- The Dexcom CGM System is approved for ages 2 years and older on the abdomen and lower back. For 18 and over, the Dexcom CGM is approved for the abdomen.
- The Dexcom CGM is compatible with iOS and Android platforms which allow glucose readings on a compatible smart device†.
- The Dexcom also has a Share feature which allows you to share your glucose readings with up to five individuals‡. By downloading the Dexcom Follow® app, followers can view your real-time glucose data directly from their smart device giving you the circle of support you need. Visit www.Dexcom.com/Dexcom-with-share for more information.
Hear from users just like you: Dexcom Warriors
*Notifications will only be received when alarms are turned on and the sensor is within 20 feet of the reading device.
† Fingersticks are required if your glucose alarms and readings do not match symptoms or when you see Check Blood Glucose symbol during the first 12 hours.
References: 1. FreeStyle Libre 2 User's Manual 2. Haak T, et al. Flash glucose-sensing technology as a replacement for blood glucose monitoring for the management of insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a multicentre, open-label randomised controlled trial. Diabetes Ther. 2017;8(1):55-73.
FreeStyle Libre 2 system:
The FreeStyle Libre 2 Flash Glucose Monitoring System is a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) device with real time alarms capability indicated for the management of diabetes in persons age 4 and older*
WARNINGS/LIMITATIONS*: The System must not be used with automated insulin dosing (AID) systems, including closed loop and insulin suspend systems. Remove the sensor before MRI, CT scan, X-ray, or diathermy treatment. Do not take high doses of vitamin C (more than 500 mg per day), as this may falsely raise your Sensor readings. Failure to use the System according to the instructions for use may result in missing a severe low blood glucose or high blood glucose event and/or making a treatment decision that may result in injury. If glucose alarms and readings from the System do not match symptoms or expectations, use a fingerstick blood glucose value to make diabetes treatment decisions. Seek medical attention when appropriate and contact Abbott Toll Free (855-632-8658) or visit* www.freestylelibre.us for detailed indications for use and safety information.
*For full indications for use and safety information, see more here.
*MDI patients with baseline A1C ≥ 8.5%
*If your glucose alerts and readings from the G6 do not match symptoms or expectations, use a blood glucose meter to make diabetes treatment decisions.
†Click here for a list of compatible smart devices
‡Do not make treatment decisions based on share and follow readings. Always confirm with your compatible smart device or Dexcom receiver.
1 Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group. Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Intensive Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes, N Engl J Med. 2008: 359(14); 1464-1476.
2 Soupal J, Petruzelkova L, Flekac M, et al. Comparison of Different Treatment Modalities for Type 1 Diabetes, Including Sensor-Augmented Insulin Regimens, in 52 Weeks of Follow-Up: A COMISAIR Study. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2016;18(9):532-538.
3 Beck RW, Riddlesworth T, Ruedy K, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: The diamond randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;317(4):371-378. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.19975.
- About Continuous Glucose Monitors
- Effect of Sensor-Augmented Insulin Pump Therapy and Automated Insulin Suspension vs Standard Insulin Pump Therapy on Hypoglycemia in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. See also Low-Glucose-Suspension Feature Cuts Severe Hypoglycemia (Free Medscape membership required).
- Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Prevention.
- Detection and treatment efficacy of hypoglycemic events in the everyday life of children younger than 7 yr.
- Hypoglycaemia, fear of hypoglycaemia and quality of life in children with Type 1 diabetes and their parents.
- Review: Continuous glucose monitoring reduces HbA1c more than self-monitoring in type 1 diabetes.
- The use and efficacy of continuous glucose monitoring in type 1 diabetes treated with insulin pump therapy: a randomised controlled trial.
- Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes.
- How continuous monitoring changes the interaction of patients with a mobile telemedicine system.
- Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Subjects With Type 1 Diabetes on Multiple Daily Injections Versus Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy.
- Continuous glucose monitoring reduces both hypoglycaemia and HbA(1c) in hypoglycaemia-prone type 1 diabetic patients treated with a portable pump.
- Sensor-augmented pump therapy from the diagnosis of childhood type 1 diabetes: results of the Paediatric Onset Study (ONSET) after 12 months of treatment.
- Quality of Life Measures in Children and Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: The Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Randomized Trial.
- Use of a real-time continuous glucose monitoring system in children and young adults on insulin pump therapy: patients' and caregivers' perception of benefit.
- Effectiveness of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in a Clinical Care Environment: Evidence from the JDRF-CGM Trial.
- Use of continuous glucose monitoring system in the management of severe hypoglycemia.
- Reducing glycaemic variability in type 1 diabetes self-management with a continuous glucose monitoring system based on wired enzyme technology.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Intensive Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes - The Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group
- Sensor-Augmented Insulin Pump Therapy: Results of the First Randomized Treat-to-Target Study.
- The Accuracy and Efficacy of Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Sensor in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes.
- Sensor-augmented pump therapy in type 1 diabetes.
- Oscillating glucose is more deleterious on endothelial function and oxidative stress than mean glucose in normals and type 2 diabetic patients.
- Accuracy of the 5-Day FreeStyle Navigator Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. Free full text available in HTML and PDF formats.
- Hypoglycemia during sleep impairs consolidation of declarative memory in type 1 diabetic and healthy humans.
- Evaluating the Clinical Accuracy of Two Continuous Glucose Sensors Using Continuous Glucose Error Grid Analysis (Diabetes Care 28:2412-2417, 2005)
- Improvement in Glycemic Excursions With a Transcutaneous, Real-Time Continuous Glucose Sensor (Diabetes Care 29:44-50, 2006)
- Awakening and Counterregulatory Response to Hypoglycemia During Early and Late Sleep.
- Defective Awakening Response to Nocturnal Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Free full text available in PDF format.
- Awakening from Sleep and Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Free full text available in PDF format.
- Impaired overnight counterregulatory hormone responses to spontaneous hypoglycemia in children with type 1 diabetes.
- Nocturnal hypoglycaemia in Type 1 diabetic patients, assessed with continuous glucose monitoring: frequency, duration and associations.
- Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Detection and Prevention of Hypoglycemia.
- Impact of Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Children and Their Families.
- Extended use of a new continuous glucose monitoring system with wireless data transmission in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus (Diabetes Technol Ther. 2006 Apr;8(2):139-45)
- Evaluation of CGMS® During Rapid Blood Glucose Changes in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes (Diabetes Technol Ther. 2006 Apr;8(2):146-55)
- Continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a single-blind, randomized, controlled trial (Pediatr Diabetes. 2006 Jun;7(3):159-64)
- Subcutaneous glucose sensor values closely parallel blood glucose during insulin-induced hypoglycaemia.
- Unrecognised hypoglycaemia in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes using the continuous glucose monitoring system: Prevalence and contributors. (J Paediatr Child Health. 2006 Dec;42(12):758-63)
- Nocturnal hypoglycaemia in Type 1 diabetic patients, assessed with continuous glucose monitoring: frequency, duration and associations.
- Continuous glucose monitoring versus self-monitoring of blood glucose in the treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus.
- The role of continuous glucose monitoring in clinical decision-making in diabetes in pregnancy.
- The Medtronic MiniMed Gold Continuous Glucose Monitoring System: An Effective Means to Discover Hypo- and Hyperglycemia in Children Under 7 Years of Age.
- Continuous Subcutaneous Glucose Monitoring System in diabetic mothers during labour and postnatal glucose adaptation of their infants.
- Glycemic Outcomes in Adults With T1D Are Impacted More by Continuous Glucose Monitoring Than by Insulin Delivery Method: 3 Years of Follow-Up From the COMISAIR Study